
Testing and Tracking – Installing and Using Google Analytics
12-Dec-2011
Wayne Sharer
In this lesson, we’ll be giving a step by step overview of how to install Google Analytics.
Google Analytics is a free analytics program provided by Google. It’s the most popular software on the internet for analytics. It provides a very comprehensive set of data on everything from visitors to traffic sources.
Sign Up for Google Analytics
Go to Google and sign up for Google Analytics.
If you already have a Google account, you can simply log into your Google account and use that account to access your analytics
If you don’t have a Google account, you’ll be asked to register a new account in the process.
When you begin the signup process, you’ll be taken to the following screen:
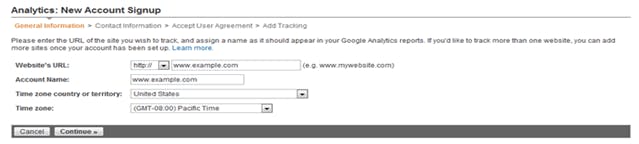
- Google Analytics Sign up Page
Enter your website URL in the first box. The second box is used purely for your own identification purposes.
Select your location and time zone then click Continue.
On the next screen, enter your name and phone number. Then click Continue.
Check yes on the screen after that to accept the terms of service.
Next you’ll be taken to a screen where you’ll be given a bunch of code you need to install on your web page.
This may seem intimidating to the non technically savvy. Fortunately, it’s much easier than it looks.
All you do is copy and paste the code into the bottom of your HTML files.
Select New Tracking Code unless you have a very compelling reason to use the Legacy Code.
Using Google Analytics
Now that you’ve got Google Analytics installed, let’s briefly go over how to use the software.
Log into your Analytics account and click “View Report” under any of your websites.
You’ll be presented with the following page:
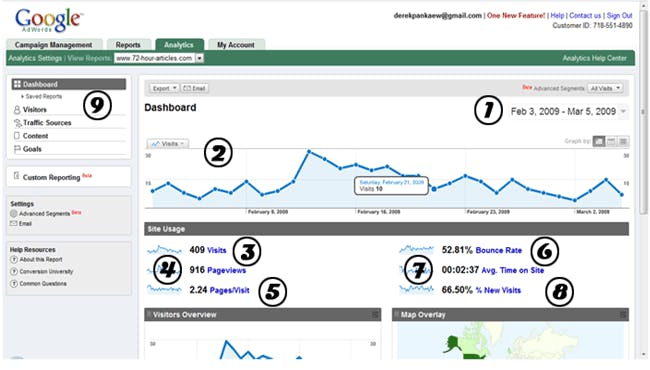
- Google Analytics Screen Shot
Here’s a rundown of this interface:
1 – Date Range. Use this dropdown box to select what date range you want to get data for. For example, if you want to see how many visitors you got in the last week; just select those dates in the dropdown box.
2 – Visitor Graph. This is a graph of how many visitors you got over the date range you selected.
3 – Visits. The number of visitors you got over the date range you selected.
4 – The number of web page views.
5 – The number of pages the average visitor visited.
6 – The bounce rate is the percentage of people who left your website without looking at another web page. In other words, they came to your front page and left right away.
7 – The average time spent on your website before leaving.
8 – What percentage of visitors are new visitors.
9 – Your dashboard where you can get more data.
The Dashboard
Under the dashboard, you’ll have three more options for getting more data: Visitors, Traffic Sources and Content.
The Visitors Menu
The visitors menu is where you can gather more data on your visitors.
Here’s some of the data you can get from this menu:
Browser – You can learn what browser your visitors use the most. This is important so that you can make sure your web page looks right on all the browsers that your visitors use.
Screen Resolution – You can learn what resolution most of your visitors have on their computers. Again, this is important for making sure you’re compatible.
Connection Speed – The connection speed of most of your visitors has a big impact on how many graphics and videos you can use.
Location – Where are most your visitors geographically located?
New or Returning – Do most of your visitors come back after the first visit?
Note: It’s very important to make sure that your browser is compatible with every screen resolution and browser that you possibly can. If you’re missing even 5%-10% because of compatibility issues, that’s a very big impact on your bottom line.
Traffic Sources Menu
This is perhaps one of the most important menus in Google Analytics. This page allows you to get detailed data on where your visitors are coming from.
By figuring out where your visitors are coming from, you have a far greater chance of increasing your traffic successfully.
Generally, it’s easier to get more traffic from a traffic source than it is to try and find a new traffic source. For example, if you’re successfully getting a lot of traffic from Google AdWords, then it’s probably a good idea to mirror your campaigns on Yahoo and MSN.
Here are some of the important statistics you can get from the Traffic Sources menu:
Overview – The first page you’ll be taken to will have an overview of your main sources of traffic. It’ll break it down by Direct Traffic, Referring Sites and Search Engines.
In addition, it will also have your top traffic sources and top keywords on the bottom of the page.
Referring Sites – If you click referring sites on the left, you can figure out which are the top websites that are sending visitors to you. If you find a website that’s working particularly well, you may want to consider trying to get even more traffic from that website.
Keywords – This is a crucial part of search engine optimization. Google Analytics will actually tell you what keywords people are using to find you.
By figuring out this data, you can improve your search engine rankings for those keywords and get even more traffic.
You can also take keywords that are doing well for you on organic search and bid on them in PPC. You could also take keywords that are doing well in PPC and optimize your site for them on search.
As you can tell, there’s a wealth of information that’s available to you. Look over your analytics carefully and extract the most valuable data.
Setup Your Analytics
Rather than continuing to read and get more information, at this point it’s best to take a break and setup your Analytics. We’ll be covering much more material in the next few lessons and it can be easy to get lost if you don’t begin implementing what you learned.
Take what you already know about setting up Google Analytics and put it into action now.
International speaker, author, and entrepreneur. Retired navy officer, former commanding officer. Over 35 years of leading, coaching, mentoring, and speaking.
Read more